Numerous projects, dozens of people and an infinite number of tasks. All those things affect project budget. But how to fit them all into a single project cost management process? We have an answer to that question!
In this article, you will find:
- The definition of project cost management
- A step-by-step project cost management process
- Techniques for estimating project costs
- The contents of a perfect project cost management plan
What Is Cost Management? Definition
Cost management is the process of estimating, planning and controling project costs throughout its duration. The main goal of this process is to ensure that planned costs won’t exceed the project budget, regardless of the circumstances.
Regardless of the industry, project cost management is one of the key factors impacting project success. Together with the delivery of high-quality requirements, it helps companies monitor their project performance and ensure the operation remains profitable.
Why is Project Cost Management Important?
Both companies and individuals set a fixed budget for a completion of significant projects, such as new investments and large purchases. In project management, things are no different.
Project cost management allows project managers to continuously monitor the expenses and ensure that they do not exceed the pre-defined limits both during and at the end of the project. As a result, this process marks a difference between project success and unwelcome consequences, with financial losses being the most severe of them. That is particularly important for larger organization with multiple projects, which, due to their quantity, are more difficult to control – and more likely to fly under the radar and become unprofitable.
Additionally, project cost management is also the key to making informed decisions. By defining and monitoring project budget, project managers can see the progress (or lack of it) and alter its course whenever necessary, minimizing risks and maximizing profitability. They are also less likely to experience unpleasant surprises in their final project report.
What’s The Difference Between Project Budget and Project Cost Management?
While project cost management and project budget might sound similar, project managers do differenciate between these two terms. The key difference between them lies in their scope and function.
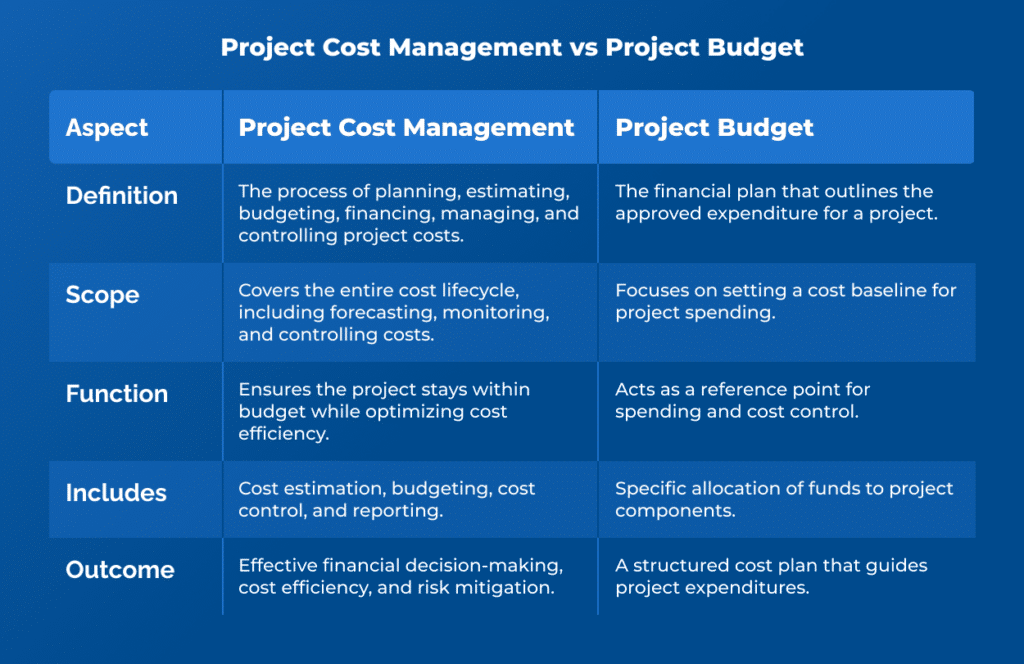
Project cost management is a comprehensive process that involves planning, estimating, budgeting, financing, managing, and controlling costs and cost performance to ensure a project is completed within financial constraints. It encompasses the entire cost lifecycle, from initial estimation to final cost tracking and reporting and is a major part of project management, regardless of the type of the project.
On the other hand, project budget is a specific financial plan that allocates costs to different project components and serves as a baseline for measuring financial performance. It is one of the outputs of cost management and represents the approved expenditure for executing the project.
Typically, a project budget template is created by project managers before the project even starts and is based on a detailed cost estimate that can then be used to compare actual costs of a project to initial assumptions.
Project Cost Management Process Step By Step
Capturing all of the actual costs of the project in cost estimation is a backbone of the project management. Unfortunately, this is not an easy task. Luckily, project cost management process can assist you with accounting for all the incomes and expenses in the project. Here’s how to complete it!
Step 1: Resource Allocation
In professional services companies, the costs of work are the most sigificant part of all the expenses. For that reason, they should be a baseline of the entire project cost management.
Before the project begins, define the entire project scope, divide it into individual deliverables, and assign people to them. Remember to account for any planned absences that might interfere with your plans, and any resources that might have to be hired. If possible, cover both positive and negative scenarios in your plans to leave some room for unexpected alterations.
Step 2: Cost Estimation
Having defined project deliverables, you can now try to estimate their costs. The best way to achieve that is by using the hourly rates of your specialists and multiplying them by the duration of each task. For assignments that are still waiting for your new hires, estimate the cost by specifying the maximum hourly rates your company is willing to pay the specialists for their services.
Then, ensure that your estimates can give you a bigger picture of your project cost management by adding additional costs to the equation. That includes both project and company overheads, such as costs of equipment, rent, bills, and support departments, i.e. marketing, administration or sales. If your company has numerous projects that share the operational costs, you can use overhead absorption rate to divide the expenses proportionally.
Last but not least, add some contingency costs to the final list of expenses in your projects. By doing so, you will ensure that no unexpected changes impact your project cost management.
Step 3: Creating a Project Budget
Based on all the information you have gathered throughout the cost management process, you can now move on to create a project budget.
To do that, take all the expenses you identified, ensure that they include the project’s fair share of organizational overheads, and add your profit margin to the equation. Then, check if the final price of the project exceeds its market value; if it does, your margin might be too high – or your project might be unprofitable in general.
An example of project budget in BigTime
Still, even the best budgets can sometimes change. Therefore, before settling on a final number, remember to leave some room for unexpected changes – project cost performance might sometimes change due to scope creep or other unforeseen changes, resulting in cost variance.
Step 4: Define Cost Control and Monitoring Methods
Project cost management doesn’t stop once a budget is approved; in fact, it has just begun, and it’s about to begin its next step: cost control.
Effective cost control ensures that project expenses remain within the approved budget while maintaining financial transparency. This step involves setting up tracking mechanisms, variance analysis, and performance measurement to manage project costs effectively. Those include:
Earned Value Management
In project cost management, earned value management is the simplest method of comparing expected use of budget with the actual data at any point on project timeline. Here’s an example of this project cost management method.
Imagine you’re managing a 10-month project with a total approved Budget at Completion, or BAC, of $100,000. The plan is simple: spend approximately $10,000 of work effort each month.
At month 5, you pause to analyze how the project is performing. According to the plan, you should have completed $50,000 worth of work by now. This figure is called the Planned Value (PV) and it represents the value of the work you intended to complete by month 5.
However, when you look at what has actually been delivered, you realize only 4 months’ worth of work is truly complete. This amounts to an Earned Value (EV) of $40,000, since the budgeted cost for that finished work is $40,000. Meanwhile, you check your expenses and see you have actually spent $45,000 to achieve that result. That’s your Actual Cost (AC).
To understand the project’s health, you calculate a few key metrics. First, you find the Cost Variance (CV):
Cost variance = EV – AC
In this case, $40,000 (EV) minus $45,000 (AC) gives you –$5,000. A negative cost variance indicates you’ve spent $5,000 more than the value of the work you’ve actually accomplished. Simply put, you’re over budget.
Next, you look at the Schedule Variance (SV), which is calculated with the following formula:
Schedule variance = EV – PV
Here it’s $40,000 minus $50,000, giving –$10,000. That tells you the project is behind schedule by $10,000 worth of work – it has only achieved 80% of what was planned by this point.
With these insights, you can see the project is both over budget and behind schedule halfway through its duration. This early warning is valuable: instead of waiting until the end to discover a costly overrun, you can now investigate causes, such as unanticipated expenses or inefficient work, and plan corrective actions. That might mean reassigning resources, adjusting timelines, renegotiating scope, or finding ways to reduce costs.
Tracking Mechanisms
Implementing reliable cost tracking tools is essential for real-time financial oversight. Professional services companies can use financial software, spreadsheets, or dashboards to monitor expenditures and compare them to the planned budget. Some of the best project management tools, including BigTime Foresight, can even create reports automatically!
Variance Analysis
To proactively address budget fluctuations, project teams must set acceptable cost variance thresholds (e.g., ±10%). Those thresholds should be monitored regularly to ensure that the project doesn’t exceed its intended budget. If actual costs exceed these thresholds, corrective actions such as fund reallocation, scope adjustments, or resource optimization should be implemented to prevent financial overruns.
Step 5: Continuously Monitor and Improve
Cost management is an ongoing process that requires continuous refinement. Regular evaluation and improvement ensure better financial efficiency in future projects.
Based on actual financial performance and lessons learned, update the plan to reflect new cost trends, market conditions, and process improvements. Additionally, after project completion, a detailed post-project financial review should be conducted to analyze budget performance, cost variances, and financial efficiencies. This insight can help improve future project budgeting and cost management strategies.
What Should a Final Project Cost Management Plan Contain?
As you can see above, the project cost management plan is a collection of various metrics and information on cost estimate, cost performance, resource planning, labor costs… The list goes on and on.
Fortunately, your cost management activities do not include creating that list. You will find it below!
Key Components of a Project Cost Management Plan
Cost Management Approach
- Defines how costs will be planned, estimated, budgeted, and controlled.
- Specifies roles and responsibilities for cost-related activities.
Cost Estimation Process
- Methods for estimating project costs (e.g., bottom-up, analogous, parametric estimating).
- Data sources for cost estimation (e.g., historical data, expert judgment).
- Assumptions and constraints affecting cost estimates.
Project Budget Development
- Breakdown of budget allocation across project phases and activities based on resource allocation of project teams.
- Inclusion of contingency reserves and management reserves.
- Process for budget approval and updates.
Cost Control Mechanisms
- Procedures for tracking actual costs versus budgeted costs.
- Thresholds and variance limits that trigger corrective actions.
- Tools and systems for real-time cost monitoring.
Funding and Cash Flow Management
- Sources of funding and financial constraints.
- Cash flow projections to ensure adequate liquidity.
- Payment schedules and invoicing processes (especially relevant for professional services).
Cost Reporting and Performance Measurement
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) for cost management.
- Frequency and format of financial reporting.
- Use of Earned Value Management (EVM) or other financial tracking techniques.
Risk Management for Cost Control
- Identification of cost-related risks (e.g., scope creep, slow project progress, market fluctuations).
- Strategies for mitigating financial risks.
- Contingency planning for unexpected cost overruns.
Change Control for Cost Adjustments
- Process for assessing and approving changes that impact costs.
- Documentation requirements for budget revisions.
- Impact analysis of changes on project financials.
How Can Project Cost Management Software Help Project Managers with This Process?
Project management tools can significantly streamline the process of creating and managing a project budget in professional services companies. These tools enhance accuracy, efficiency, and financial visibility by automating calculations, tracking expenses, and integrating resource allocation.
Additionally, tools such as BigTime also offer cost estimation, budgeting, tracking, and reporting, ensuring that projects stay within financial constraints while improving efficiency and transparency. These tools integrate financial data, automate calculations, and provide real-time insights that support informed decision-making, making budgeting faster and more proactive than ever.
Precise Cost Estimate and Project Management in a Single Tool? It’s Possible with BigTime!
Management is the process consisting of a constant exchance of current and historical cost data. With BigTime, it’s simpler than ever!
BigTime bridges the gap between resources and finances by using pre-defined rates to create accurate estimates and error-free project budget automatically, and updating it every time you make a change to your plans. It will also generate automated reports, helping project managers avoid mistakes and create perfect budgets.
Sounds good? See what else BigTime can do for you – book a demo now!